The Changing Distribution of Goods and Services in GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is the total market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given year. GDP is a measure of the size of an economy and is often used to compare the economic output of different countries.
GDP can be divided into two components: goods and services. Goods are tangible products that can be bought and sold, such as cars, computers, and food. Services are intangible products that are provided by businesses, such as haircuts, doctor's visits, and transportation.
The distribution of goods and services in GDP has changed over time. In the early 1900s, the majority of GDP was generated by goods. However, the share of services in GDP has been increasing steadily since then. In 2022, services accounted for about 70% of GDP in the United States.
Changing from goods to services in GDP
There are a number of factors that have contributed to the shift from goods to services in GDP. One factor is the rise of technology. Technology has made it possible to produce goods more efficiently, which has led to a decrease in the demand for labor in the manufacturing sector. As a result, many manufacturing jobs have been lost, and the share of GDP generated by goods has declined.
Another factor that has contributed to the shift from goods to services is the aging population. As the population ages, there is a greater demand for services such as healthcare, education, and retirement care. These services are not as easily traded internationally as goods, so they tend to be produced domestically, which increases the share of GDP generated by services.
Economic implications of changing distribution in GDP
The shift from goods to services has a number of implications for the economy. One implication is that the demand for skilled workers has increased. Services tend to be more knowledge-intensive than goods, so businesses need workers with the skills to provide these services. This has led to an increase in wages for skilled workers and a decrease in wages for unskilled workers.
Another implication of the shift from goods to services is that the economy has become more globalized. Services are often easier to trade internationally than goods, so businesses have been able to expand their operations into new markets. This has led to increased competition and lower prices for consumers.
The shift from goods to services is a trend that is likely to continue in the future. As technology continues to advance and the population ages, the demand for services is likely to continue to grow. This will have a number of implications for the economy, including increased demand for skilled workers and increased globalization.
Supporting Data
The following data illustrates the change in the distribution of goods and services in GDP over time:
- In 1900, goods accounted for about 80% of GDP in the United States.
- In 2000, goods accounted for about 60% of GDP in the United States.
- In 2022, goods accounted for about 30% of GDP in the United States.
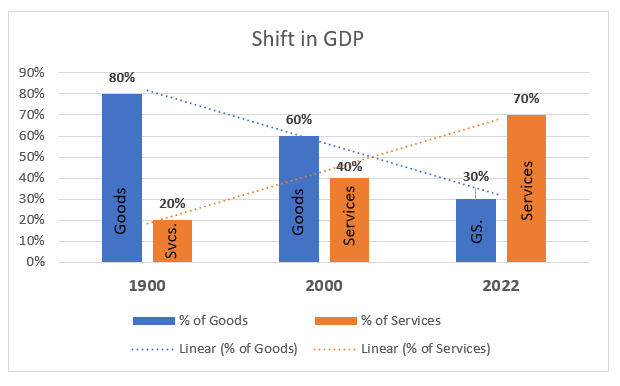
The data shows that the share of GDP generated by goods has declined steadily over time. This decline is due to a number of factors, including the rise of technology, the aging population, and globalization.
For small businesses that are currently in the goods category, the shift in GDP towards services can have concerning implications. As the demand for goods continues to decline, small businesses that rely on the production and sale of tangible products may face a decrease in demand for their products, which could lead to lower revenue and decreased profitability.
Responding to changing distribution in GDP
In response to these challenges, small businesses in goods categories should consider diversifying their product offerings to include services to remain competitive. For instance, a small business that manufactures furniture can diversify their product offerings by offering interior design services. They can also partner with real estate companies to stage and showcase their furniture products in homes that are up for sale.
Small businesses can also explore expanding their product offerings to include technological products, as technology is playing an increasingly important role in the economy. Additionally, small businesses have the opportunity to take advantage of the growing demand for skilled workers by investing in the training of their employees and hiring individuals with skills that are in high demand, such as data analytics, e-commerce, and logistics.
Furthermore, small businesses in the goods category can partner with service-oriented businesses to collaborate and explore new opportunities, including expanding into new markets or developing new products that cater to the needs of a service-oriented customer base.
In conclusion, small businesses in the goods category should be aware of the changing distribution of goods and services in GDP and take proactive steps to remain competitive in the evolving economy. By diversifying their product offerings, investing in technology and workforce training, and partnering with service-oriented businesses, small businesses can adapt to changing customer demands and remain relevant in the marketplace.